In recent years, fingerprint-based authentication has become a popular security measure in smartphones, providing users with a convenient and quick way to unlock their devices. However, a new vulnerability known as the BrutePrint attack has emerged, exposing the weaknesses in this biometric security method.
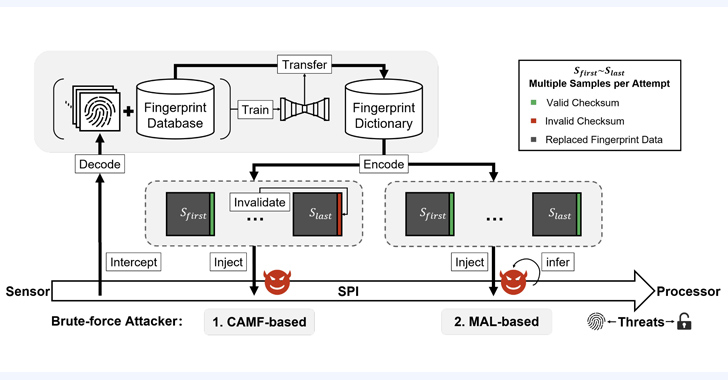
BrutePrint attack is a technique that allows attackers to unlock smartphones by brute-forcing the fingerprint authentication. Unlike previous attacks that focused on bypassing or spoofing the fingerprint sensor, BrutePrint attack exploits the limited number of attempts allowed by the device before it locks down.
How does the BrutePrint Attack work?
When a user sets up fingerprint authentication on their smartphone, the device stores a digital representation of their fingerprint called a "template." This template is used to verify the user's fingerprint each time they attempt to unlock the device. The BrutePrint attack takes advantage of the fact that some smartphones do not impose any restrictions on the number of fingerprint authentication attempts.
An attacker attempting the BrutePrint attack would need physical access to the targeted smartphone. They would systematically generate and attempt different fingerprint templates until a match is found, effectively bypassing the device's security measures. This attack can be automated, using software tools that simulate multiple fingerprint attempts rapidly.
Implications and Mitigation
The BrutePrint attack poses a significant threat to smartphone security, as it undermines the reliability of fingerprint authentication. While it requires physical access to the device, it could potentially compromise sensitive data stored on the smartphone, such as personal information, financial data, or private communications.
Smartphone manufacturers and software developers need to address this vulnerability urgently. Implementing stricter limitations on the number of authentication attempts can help mitigate the risk of BrutePrint attacks. Additionally, multifactor authentication methods, such as combining fingerprint recognition with a PIN or password, can provide an added layer of security.
It is crucial for smartphone users to remain vigilant and keep their devices secure. Regularly updating the device's software and installing security patches can help protect against known vulnerabilities. Furthermore, users should consider using strong alphanumeric passcodes as an alternative to relying solely on fingerprint authentication.
Conclusion
The emergence of the BrutePrint attack highlights the importance of continually improving smartphone security. While fingerprint authentication has offered a convenient and secure method of unlocking devices, vulnerabilities like the BrutePrint attack remind us that no security measure is entirely foolproof. It is essential for manufacturers, developers, and users to stay informed about emerging threats and work together to strengthen smartphone security and protect sensitive data.
Comments
Post a Comment