North Korea's APT37 Targets Southern Counterpart with M2RAT Malware: Highlighting Ongoing Threat of Cyber Espionage and Need for Vigilance
North Korea's Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) group, APT37, has reportedly been targeting their southern counterpart with a new malware strain known as M2RAT. This latest attack highlights the continued threat posed by North Korea's cyber espionage capabilities and their efforts to undermine South Korean national security.
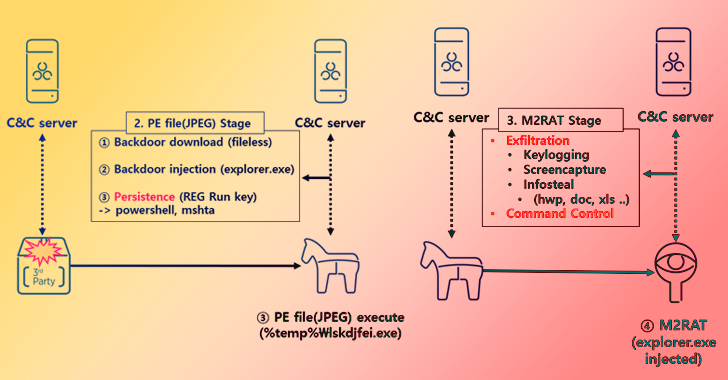
According to reports, the M2RAT malware has been observed in a spear-phishing campaign that targeted the Korean government, as well as other high-profile targets in the region. The attack began with a spear-phishing email that contained a malicious attachment, which when opened, installed the malware on the victim's computer.
Once installed, M2RAT creates a backdoor that allows the attacker to gain full access to the victim's computer and steal sensitive information. The malware also contains keylogging capabilities, enabling the attacker to capture the victim's keystrokes and potentially obtain login credentials to important systems and applications.
APT37 has been active for several years and is known for its sophisticated cyber espionage capabilities. The group has been linked to a number of high-profile attacks, including the 2017 WannaCry ransomware attack that affected hundreds of thousands of computers worldwide.
While North Korea has denied involvement in any cyber attacks, there is growing concern over the country's cyber capabilities and the threat they pose to national security. The use of M2RAT highlights the continued threat of cyber espionage and the need for heightened vigilance in protecting sensitive information.
In response to the attack, South Korea has reportedly launched an investigation and taken steps to strengthen its cyber defenses. The government has urged organizations to be vigilant in their cybersecurity efforts and to report any suspicious activity to the relevant authorities.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, it is important for organizations to implement strong security measures to protect against potential attacks. This includes implementing multi-factor authentication, regularly updating software and security patches, and providing employee education and training to recognize and respond to potential threats.
In conclusion, the use of M2RAT by APT37 is another example of the ongoing threat posed by North Korea's cyber espionage capabilities. While the attack targeted South Korea, it serves as a reminder of the importance of strong cybersecurity measures and the need for continued vigilance in protecting against potential attacks.
Comments
Post a Comment