Titan Stealer is a newly discovered information stealer malware that is written in the Go programming language (Golang). It is primarily designed to steal sensitive information from infected computers, such as login credentials, financial information, and personal data. This information can then be sold on underground forums or used for financial gain.
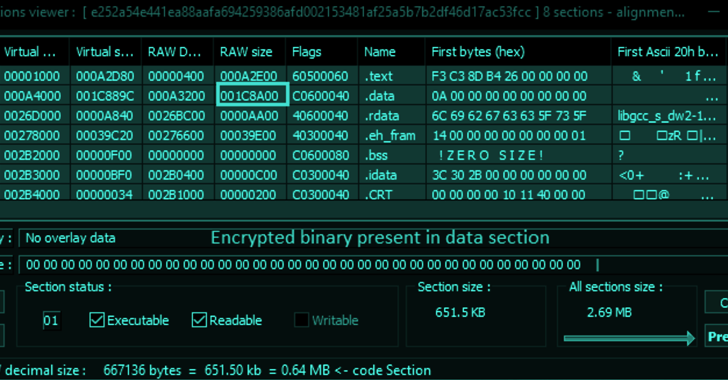
One of the key features of Titan Stealer is its ability to evade detection by security software. It uses advanced obfuscation techniques to hide its activity, making it difficult for anti-virus software to detect and remove it. Additionally, it is highly customizable, allowing cybercriminals to add new components and features as needed.
Another feature that sets Titan Stealer apart from other information stealer malware is its use of Golang. Golang is a relatively new programming language that has gained popularity in recent years due to its high performance and ease of use. However, it is also relatively unknown to security researchers, making it a target-rich environment for cybercriminals.
To protect against Titan Stealer and other information stealer malware, organizations should implement multi-layer security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and anti-virus software. Additionally, employees should be trained on the importance of not opening suspicious emails or attachments, and organizations should implement strict email filtering and monitoring policies.
Organizations should also be vigilant in their security practices, regularly checking their systems for signs of compromise and responding quickly to any detected threats. This can include conducting regular penetration tests and vulnerability scans, as well as implementing security best practices, such as regular software updates and patch management.
In conclusion, Titan Stealer is a new and evolving threat that should be taken seriously by organizations of all sizes. Its use of Golang and advanced obfuscation techniques make it a persistent threat that requires constant vigilance and robust security measures to protect against.
Comments
Post a Comment